Let Us Know How We Can Help. We Are Your Dedicated Solutions Provider.
Top 10 Printed PCB Board Types for Your Electronics Projects
When embarking on electronics projects, one of the fundamental components that engineers and hobbyists alike rely on is the printed PCB board. Versatile and essential, printed circuit boards serve as the backbone of electronic devices, providing not only a platform for connecting various electronic components but also ensuring that they function cohesively. The breadth of available printed PCB board types allows individuals to select designs best suited for their specific applications, whether it's a simple LED circuit or a complex microcontroller project.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 printed PCB board types, highlighting the unique characteristics and applications of each. By understanding the distinct features of these printed circuit boards, readers will be better equipped to make informed decisions when designing their own electronic systems. This comprehensive overview will serve as a valuable guide for anyone looking to delve deeper into the world of printed PCBs and elevate their electronics projects to the next level. Whether you're a novice or an experienced engineer, having insight into the different types of printed PCB boards will ultimately enhance your project's efficiency and functionality.
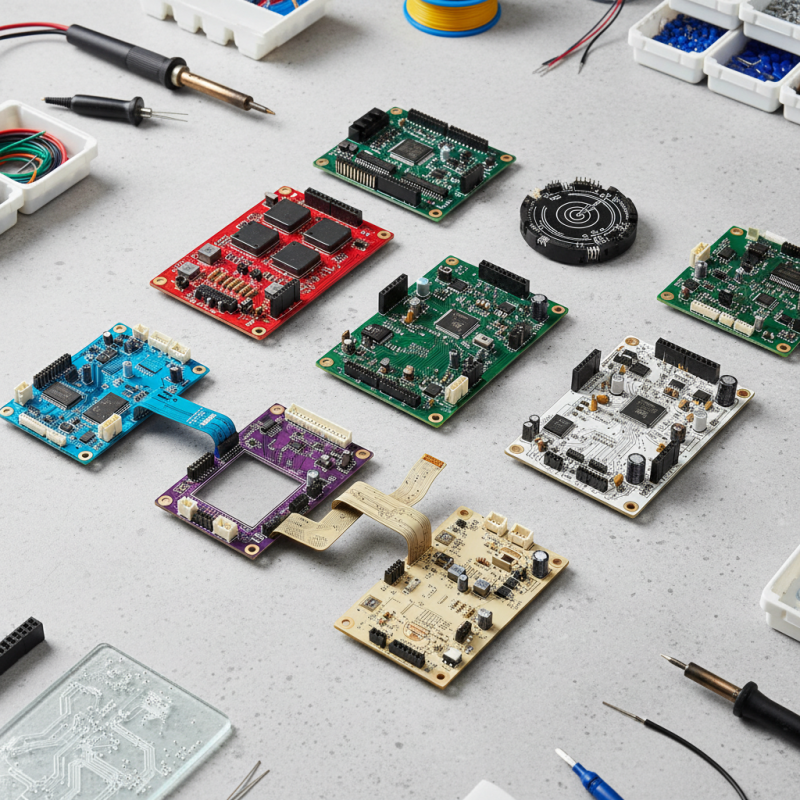

Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding PCB Basics: What is a Printed Circuit Board?
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as the backbone of most electronic devices, providing a critical structure for mounting and interconnecting components. A PCB consists of a flat board, typically made from insulating material like fiberglass, with conductive pathways etched into its surface. These pathways are designed to facilitate the flow of electricity between various electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. By organizing these circuits in a compact form, PCBs enable efficient connections while minimizing the risk of short circuits, which can lead to device failure.
Understanding the basics of PCBs is essential for anyone delving into electronics projects. There are various types of PCBs, each tailored to specific applications, such as single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. Each type offers unique advantages, catering to different complexities and sizes of projects. For beginners, starting with a basic single-sided PCB might be ideal, as it provides hands-on experience with the fundamental concepts of circuit design and assembly, while more advanced users may opt for multilayer boards for intricate designs. Overall, mastering PCB fundamentals lays the groundwork for successful electronics development, allowing creators to innovate and bring their ideas to life.
Top 10 Printed PCB Board Types for Your Electronics Projects
Types of Printed PCB Boards: An Overview of Options Available
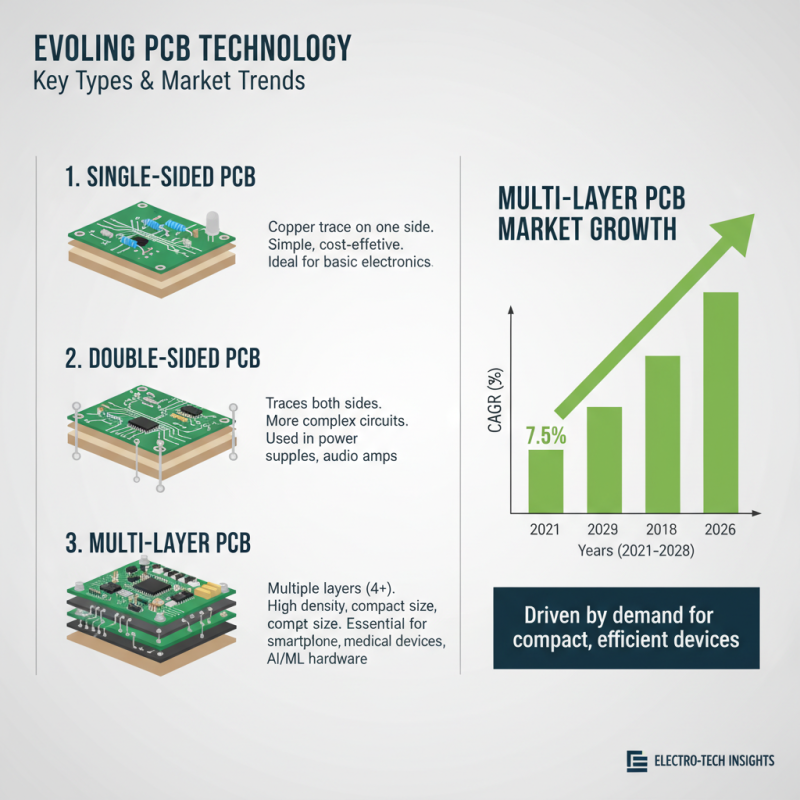
When embarking on electronics projects, understanding the types of printed PCB (Printed Circuit Board) options available can significantly influence both performance and cost-effectiveness. The most common types include single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs. According to industry reports, the multi-layer PCB market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 7.5% from 2021 to 2028, driven by the increasing demand for compact and efficient electronic devices. This growth emphasizes the need for designers to consider how multi-layer designs can accommodate complex circuits within smaller footprints.
Another type worthy of mention is the flexible PCB, which has seen a spike in usage across various sectors, particularly in mobile devices and wearables. As indicated in recent market analyses, the flexible PCB sector is expected to witness significant growth, supported by advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. When selecting the right type of PCB, it is essential to assess the project’s specific requirements, including size constraints, thermal management, and component density.
Tip: Always prototype a simpler version of your design before scaling up. This not only saves costs but also helps identify potential issues early in the process. Moreover, consider using design software that can simulate electrical performance for various PCB types, enhancing your overall project efficiency. Choose wisely to achieve the best results in your electronic endeavors.
Flexible PCBs: Advantages and Applications in Electronics
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have gained significant traction in the electronics industry due to their unique advantages and diverse applications. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs are manufactured using pliable materials that can conform to different shapes and fit in tight spaces. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global flexible PCB market is expected to reach USD 35 billion by 2026, emphasizing the growing demand for these versatile components in various sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare.
One of the primary advantages of flexible PCBs is their lightweight nature, which reduces the overall weight of electronic devices, crucial for portable applications. Additionally, their ability to withstand bending and twisting makes them ideal for wearables and other compact devices. A study published in IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Technology highlighted that flexible PCBs can improve the reliability of electronic assemblies, reducing the risk of failure due to mechanical stress. This reliability paired with ease of integration into complex systems positions flexible PCBs as a vital component in the evolution of modern electronics, enabling innovations that push the boundaries of design and functionality.
Top 10 Printed PCB Board Types for Your Electronics Projects
| PCB Type | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid PCB | Durable, cost-effective, and great for high-density designs. | Consumer electronics, computer hardware. |
| Flexible PCB | Lightweight, space-saving, and can be bent or twisted. | Wearable devices, medical equipment. |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Combines benefits of rigid and flexible designs. | Aerospace, military applications. |
| High-Frequency PCB | Designed for RF applications, minimal signal loss. | Telecommunications, satellite systems. |
| Metal-Core PCB | Excellent heat dissipation for high-power applications. | LED lighting, power supplies. |
| Multilayer PCB | Increased density and functionality in compact spaces. | Computers, advanced electronic devices. |
| Double-Sided PCB | Cost-effective for basic applications, easy to assemble. | Basic electronic devices, appliances. |
| Embedded Component PCB | Allows components to be integrated into the board. | Smart devices, consumer electronics. |
| High-Density Interconnector (HDI) PCB | Offers fine lines and spaces for advanced applications. | Mobile devices, high-performance electronics. |
Rigid PCBs: Stability and Performance for Complex Circuits
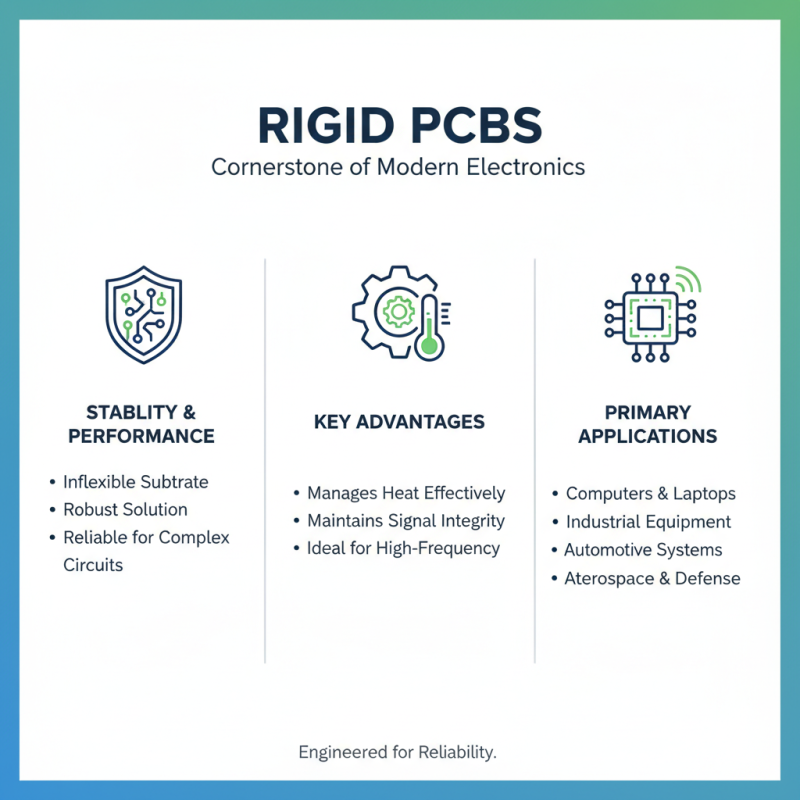
Rigid PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are a cornerstone in the design and manufacturing of modern electronics, particularly when stability and performance are paramount. These boards, characterized by their inflexible substrate, offer a robust solution for complex circuits that demand reliability. Thanks to their solid structure, rigid PCBs can effectively manage heat and maintain signal integrity, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and demanding environments.
When designing with rigid PCBs, it's crucial to consider factors such as layer count and material choice. More layers can accommodate complex designs but require more careful planning to avoid issues like signal interference. Additionally, selecting the right material can influence the board’s thermal properties and overall durability.
**Tips:** Ensure that your layout is optimized for the best thermal management by including copper pour areas and thermal vias to dissipate heat effectively. Furthermore, always run simulations on your circuit designs to catch potential issues before fabrication. Regular design reviews can also help in identifying areas for improvement, ensuring that your final product meets performance and reliability standards.
Multilayer PCBs: Enhancing Functionality in Compact Designs
Multilayer PCBs have revolutionized the landscape of electronics design by offering enhanced functionality in compact spaces. Unlike traditional single-layer boards, multilayer PCBs enable the stacking of multiple conductive layers, which allows designers to achieve greater complexity without increasing the board's footprint. This is particularly beneficial for modern applications where size and performance are critical, such as in smartphones, wearable technology, and advanced computing devices.
The key advantage of utilizing multilayer PCBs lies in their ability to effectively manage intricate routing and component placement. By incorporating multiple layers, designers can segregate power and ground planes, minimize electromagnetic interference, and significantly improve signal integrity. Furthermore, the dense interconnection capabilities of multilayer boards facilitate the integration of sophisticated functionalities, catering to the rising demand for high-performance electronics. This trend not only maximizes board efficiency but also aligns with the industry's push towards miniaturization, making multilayer PCBs an essential choice for engineers looking to innovate in compact design environments.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Designing High-Quality Printed PCB Boards Efficiently
-
Why Printed PCBs Are Essential for Modern Electronics Innovation
-
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Circuit Box for Your Needs
-

The Future of Electronics: How PCB and Assembly Technology is Shaping Tomorrow's Devices
-

Why Effective Board Design Matters for Successful Business Strategies
-

Why Printed Board Assembly is Essential for Modern Electronics Manufacturing
