Let Us Know How We Can Help. We Are Your Dedicated Solutions Provider.
Top 10 Tips for Effective Circuit Board Design Strategies?
In the world of electronics, effective circuit board design is crucial. It serves as the backbone of nearly every electronic device we use today. However, many designers struggle with some key aspects. Understanding the nuances of circuit board design can significantly enhance performance and reliability.
The complexity of these designs can be overwhelming. Designers often face challenges like signal integrity, thermal management, and routing efficiency. Mistakes can lead to costly delays and product failures. Therefore, careful consideration of various strategies is essential in developing successful circuit boards.
Exploring proven tips can help improve the design process. These strategies aim to refine layouts, enhance functionality, and ensure manufacturability. By embracing best practices in circuit board design, you can avoid common pitfalls and create robust products that meet consumer needs. Think of design as a blend of art and science, where mistakes offer valuable lessons for the next project.

Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding the Fundamentals of Circuit Board Design Principles
Effective circuit board design hinges on understanding core principles. Knowledge of signal integrity is vital. This includes managing electromagnetic interference. Using proper routing techniques can help mitigate issues. Ensure traces are not excessively long. Also, consider the thickness of your traces. Thicker traces can carry more current.
Power distribution also plays a crucial role. A solid ground plane can reduce electrical noise. It acts as a reference point for signals. Utilize decoupling capacitors effectively to smooth power delivery. Balance the layout; avoid placing power and signal traces too close. This can lead to unintentional coupling and interference.
Finally, color coding your design can enhance clarity. While it's easy to overlook this detail, it helps in identifying connections and troubleshooting. Mistakes can occur even in the best designs, leading to revisions. Embrace these challenges; they foster growth in your design capabilities. The journey of refining circuit board design is ongoing and demands patience.
Incorporating Industry-Specific CAD Tools for Enhanced Layout Standards
Incorporating industry-specific CAD tools is key for effective circuit board design. These tools streamline the workflow and improve accuracy. They also provide features tailored to specific applications, enhancing the design process. For example, thermal simulation can identify hot spots early. This is crucial for preventing failures in high-performance circuits. However, designers often overlook these tools, leading to inefficiencies.
Using CAD tools can be daunting. The learning curve is real, and many users face challenges. It's common to feel overwhelmed by the myriad of features. Sometimes, mistakes occur simply due to unfamiliarity. A lack of knowledge about the software can lead to suboptimal designs. Designers should prioritize training and experimentation. Engaging in collaborative projects can also help build confidence and skill.
Caring for details is essential. Small errors can snowball into bigger issues, affecting functionality. Designers need to constantly review their work. Regular check-ins and iterative designs can save time later. Embracing an adaptive mindset while using CAD tools will enhance creativity. However, it’s easy to become complacent with basic techniques. Continuous learning is vital in this ever-evolving field.
Top 10 Tips for Effective Circuit Board Design Strategies
Best Practices for Signal Integrity and Noise Reduction Techniques
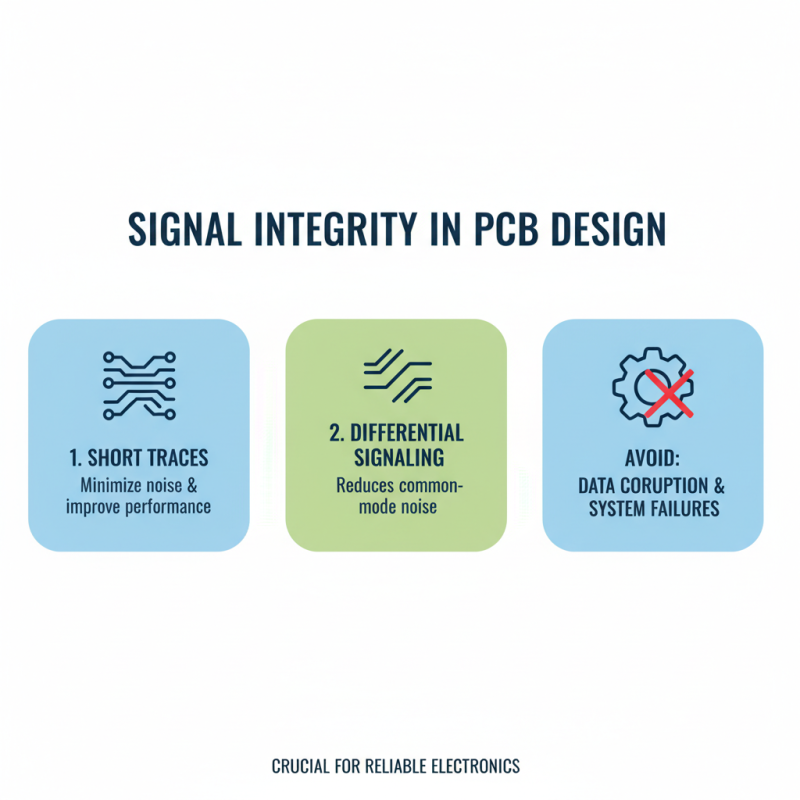
When designing circuit boards, signal integrity is crucial. Poor design can lead to data corruption and system failures. Start with carefully routing traces. Keep them as short as possible. Longer traces can pick up noise and reduce performance. Use differential signaling where feasible. This method helps to cancel out noise between the two signals.
Ground planes are essential in maintaining signal integrity. They provide a return path for signals, reducing electromagnetic interference. Ensure the ground plane is solid and undisturbed by other elements. It may seem tedious, but testing the plane design can reveal flaws. Many overlook this step, leading to unexpected problems later.
Noise reduction techniques should not be ignored. Capacitors can be used to filter out unwanted signals. Place them near components that generate high-frequency noise. Furthermore, shield sensitive traces with ground or power planes. It may seem excessive, but the results will speak for themselves. Attention to detail in these areas can turn a mediocre design into an effective one.
Optimizing Component Placement for Thermal Management and Reliability
When designing circuit boards, component placement is crucial for thermal management and reliability. Studies show that nearly 30% of circuit failures stem from thermal issues. A well-thought-out layout can minimize heat hotspots. Components generating high heat should be spaced apart. This practice promotes airflow and reduces thermal bottlenecks.
Another critical aspect is the proximity of heat-sensitive components. For instance, if a power regulator is too close to sensitive chips, it can cause malfunctions. Proper alignment and spacing can enhance performance. The IPC standard suggests keeping heat-generating parts at least 10mm apart from delicate components.
However, achieving this isn't always straightforward. Designers often face challenges like space constraints. Balancing thermal management with a compact design can lead to compromises. Some may overlook thermal vias, which are essential for effective heat dissipation. Awareness of these factors plays a key role in creating reliable designs that withstand thermal cycling and extend the product's lifespan.
Implementing Design Review Processes to Minimize Manufacturing Errors
Implementing design review processes is crucial to minimizing manufacturing errors in circuit board design. Research from IPC reveals that over 80% of design defects originate in the early stages. To tackle this issue, comprehensive design reviews should be standard practice. A collaborative approach allows for multiple perspectives, enhancing the quality of the final product.
Tip: Schedule regular review meetings with your design team. This fosters open communication and encourages the sharing of different viewpoints. Regular checks can identify issues before they escalate. Utilize feedback from engineers and manufacturers, as they often spot problems the design team might overlook.
Incorporating real-world scenarios into the design review process can also be beneficial. Encourage designers to simulate potential manufacturing pitfalls. For example, understanding the thermal dynamics of a circuit board can prevent overheating issues. A study indicated that boards that undergo thorough simulation can decrease revision cycles by up to 25%.
Tip: Document every design iteration and stakeholder feedback. This creates a knowledge base. It helps identify recurring issues and supports continuous improvement. Designers must reflect on previous mistakes to avoid repeating them. It isn’t just about following the process; it’s about learning from it.
Related Posts
-
2025 Guide: How to Master Circuit Board Design for Beginners
-
Ultimate Guide to PCB Design and Assembly Best Practices for Beginners
-

The Future of Electronics: How PCB and Assembly Technology is Shaping Tomorrow's Devices
-
2025 How to Choose the Best Circuit Board Components for Your Projects
-
Top PCB Assembly Trends to Watch in 2025 for Electronics Manufacturers
-

What is PCB and Assembly Process Explained for Beginners
